Description
This detailed product description for "Tongue Tie" is designed to inform, educate, and guide individuals who may be researching or experiencing this condition, positioning awareness and professional consultation as the ultimate "product."
Tongue Tie (Ankyloglossia) - Comprehensive Guide & Support
Unlocking a World of Better Health and Function
Tongue tie, medically known as ankyloglossia, is a congenital condition present from birth, where an unusually short, thick, or tight band of tissue (the lingual frenulum) tethers the bottom of the tongue's tip to the floor of the mouth. This restriction can significantly impede the tongue's normal range of motion, leading to a cascade of challenges for individuals across all ages – from newborns struggling to feed, to children facing speech difficulties, and adults experiencing discomfort or sleep issues.
Our comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the complexities of tongue tie, empower you with knowledge, and connect you with the resources needed to effectively diagnose and address this often-misunderstood condition.
Why Addressing Tongue Tie Matters: The Benefits of Proper Tongue Function
The tongue is a remarkably powerful and versatile muscle, crucial for feeding, speech, swallowing, breathing, and even the development of the jaw and airway. Ensuring its proper function by addressing a tongue tie can lead to profound improvements:
- Improved Feeding & Nutrition: For infants, overcoming latching difficulties leads to efficient milk transfer, better weight gain, and a more comfortable breastfeeding experience for both baby and mother.
- Enhanced Speech Development: Unrestricted tongue movement allows for the clear articulation of sounds, promoting confidence and effective communication.
- Better Oral Health & Development: Proper tongue posture supports ideal palatal development, reduces the risk of dental crowding, gum recession, and helps maintain oral hygiene.
- Relief for Breastfeeding Mothers: Eliminates nipple pain, trauma, and secondary complications like mastitis, enabling a successful and enjoyable breastfeeding journey.
- Prevention of Long-Term Issues: Early intervention can prevent future problems such as sleep-disordered breathing (snoring, sleep apnea), jaw pain (TMJ/TMD), digestive issues, and even postural imbalances.
- Increased Comfort & Quality of Life: From improved eating habits to reduced mouth breathing and enhanced self-esteem, releasing a tongue tie can significantly boost overall well-being.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Tongue Tie Across Age Groups
Identifying tongue tie can be challenging as symptoms vary depending on age and severity. It's crucial to be aware of the potential indicators:
In Infants & Babies:
- Difficulty Latching: Poor or shallow latch during breastfeeding, inability to create a strong suction.
- Clicking Sounds: Audible clicking during feeding, indicating loss of suction.
- Poor Weight Gain: Baby struggles to gain weight due to inefficient milk transfer.
- Prolonged Feeding Times: Feeds lasting an hour or more, or very frequent feeds.
- Fussiness at the Breast: Baby pulls off, cries, or seems frustrated during feeds.
- Reflux or Excessive Gas: Due to swallowing air during inefficient feeds.
- Nipple Pain/Damage for Mother: Cracked, bruised, or misshapen nipples; recurrent mastitis or low milk supply.
- Inability to Stick Tongue Out: Tongue cannot extend past the lower lip or even beyond the gum line.
- Tongue Appearance: Tongue may appear heart-shaped, notched, or have a divot when extended.
- Oral Discomfort: Baby may appear to have a "tight" mouth or struggle with oral motor movements.
In Children & Adults:
- Speech Difficulties: Lisp, difficulty with sounds requiring tongue elevation (e.g., 'r', 'l', 't', 'd', 'n', 's', 'z').
- Eating Challenges: Difficulty chewing, swallowing, licking an ice cream cone, clearing food from teeth, or gagging on certain textures.
- Dental Issues: Gaps between front teeth, gum recession, increased risk of cavities, challenges with orthodontics (difficulty retaining results).
- Mouth Breathing & Sleep Issues: Chronic mouth breathing, snoring, sleep apnea, due to a tongue that can't rest properly on the roof of the mouth.
- Jaw Pain (TMJ/TMD): Compensation from jaw muscles due to restricted tongue movement.
- Headaches & Neck Tension: Related to compensatory muscle strain.
- Social Embarrassment: Due to speech impediments or difficulties with public eating.
- Difficulty Kissing or Playing Wind Instruments: Limited tongue mobility affecting various activities.
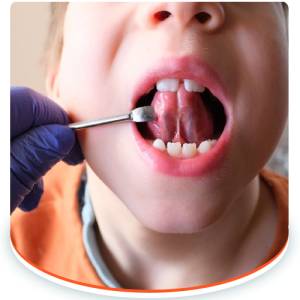
Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Approach
Diagnosis of tongue tie involves more than just a visual inspection. A thorough assessment includes:
- Visual Inspection: Observing the lingual frenulum's appearance, thickness, and attachment points.
- Functional Assessment: Evaluating the tongue's range of motion, ability to elevate, lateralize (move side-to-side), and extend, as well as its impact on feeding or speech.
- Professional Consultation: Seeking evaluation from healthcare professionals specializing in tongue tie, such as:
- Lactation Consultants (IBCLC) for infants.
- Pediatricians or Family Physicians.
- Pediatric Dentists or Airway-Focused Dentists.
- ENT Specialists (Otolaryngologists).
- Speech-Language Pathologists.
- Myofunctional Therapists.
Treatment Options: Releasing the Restriction
Once diagnosed, the primary treatment for functional tongue tie is a procedure to release the frenulum:
Frenotomy (Frenectomy):
- A simple, quick procedure to release the tight frenulum.
- Method 1: Scissors: Typically performed in office, especially for infants, by a trained physician or dentist. It involves a quick snip of the frenulum. Local anesthetic may or may not be used.
- Method 2: Laser: A laser can be used to ablate (vaporize) the tissue, often resulting in minimal bleeding and a precise release. This is commonly used in dental or specialist offices.
- The procedure aims to free the tongue, allowing for a significantly improved range of motion.
Frenuloplasty:
- For more complex or thicker frenula, or in older children/adults, a frenuloplasty might be recommended. This is a more involved surgical procedure, often requiring sutures, and may be performed under local or general anesthesia.
Post-Procedure Care & Holistic Support
The release of a tongue tie is often just one step in the journey. Comprehensive post-procedure care is vital for optimal results:
- Wound Care & Stretches: Specific stretches and exercises are crucial to prevent reattachment and ensure proper healing and mobility.
- Lactation Support: For infants, follow-up with a lactation consultant is essential to re-establish effective feeding patterns.
- Myofunctional Therapy: For children and adults, myofunctional therapy helps retrain the tongue and facial muscles to achieve proper resting posture, swallow patterns, and breathing.
- Speech Therapy: May be necessary for older children and adults to correct speech patterns developed over years of compensation.
- Osteopathic or Chiropractic Care: Some patients benefit from bodywork to release compensatory tension in the head, neck, and jaw.
Take the First Step Towards Relief
If you suspect tongue tie in yourself, your child, or a loved one, don't wait. Early intervention is key, especially for infants, to prevent the development of compensatory habits and long-term health issues.
Contact a qualified healthcare professional today to discuss your concerns and explore diagnostic and treatment options. Empower yourself with information and take action towards improved health, comfort, and quality of life.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis, treatment, and medical advice related to your specific condition or concerns.