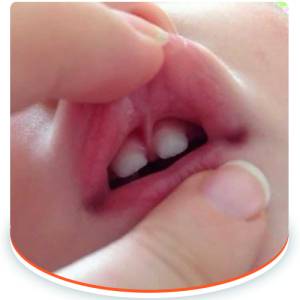
A Lip Tie (clinically known as a restricted labial frenum) refers to a condition where the thin piece of tissue connecting the upper lip to the gum line (the superior labial frenum) is unusually thick, short, or extends too far down. This restriction can severely limit the mobility of the upper lip, impacting various functions from infancy through adulthood.
Often overlooked or misdiagnosed, a lip tie can have profound effects on feeding, oral hygiene, speech development, and overall comfort. Our aim is to provide comprehensive information, encourage early diagnosis, and highlight effective solutions for individuals affected by this condition.
Understanding the impact of a lip tie is the first step towards relief. This "product" (information & solution pathway) addresses the following critical issues:
1. Infant Feeding Difficulties: * Poor Latch: Babies struggle to flare their upper lip properly, preventing a deep, effective latch during breastfeeding. * Nipple Pain/Damage for Mother: Shallow latch can cause significant pain, cracking, and even bleeding for breastfeeding mothers. * Inefficient Milk Transfer: Babies may take longer to feed, tire easily, and not get enough milk, leading to poor weight gain. * Excessive Air Intake: Restricted lip movement can lead to increased swallowing of air, causing gas, reflux, fussiness, and colic symptoms. * Clicking Sounds: Audible clicking during feeding often indicates a poor seal. * Dribbling Milk: Inability to maintain a seal can result in milk leaking from the corners of the mouth.
2. Oral Hygiene & Dental Health Concerns: * Difficulty Cleaning: The tight frenum can make it challenging for parents (and later, the child) to properly clean the gum line and front teeth, increasing the risk of cavities (especially "milk rot" or early childhood caries). * Diastema (Gap): A prominent lip tie can pull the gum tissue down, creating or exacerbating a gap between the two front upper teeth. * Gum Recession: In some cases, the tight frenum can pull on the gum tissue, leading to recession over time.
3. Speech Development Impacts: * While less directly impactful than tongue tie, a severe lip tie can sometimes restrict lip movement enough to affect the articulation of certain sounds that require full lip mobility.
4. Social & Comfort Issues: * Older children or adults may feel self-conscious about a noticeable gap between their front teeth caused by a prominent frenum. * Chronic discomfort from the tight tissue.
1. Comprehensive Assessment: * A thorough oral examination by a trained healthcare professional (e.g., pediatric dentist, ENT, oral surgeon, experienced lactation consultant, or doctor familiar with ties) is crucial. They will assess the appearance and function of the frenum, often looking at both the upper lip and tongue (as lip and tongue ties frequently co-occur).
2. Targeted Treatment (Frenectomy/Frenuloplasty): * If a functional impairment is identified, a procedure called a frenectomy (or frenuloplasty) is often recommended. This is a quick and minimally invasive procedure that releases the restrictive tissue. * Methods Include: * Scalpel or Scissors: A traditional surgical approach. * Diode Laser: A common modern technique that offers precision, minimizes bleeding, and can reduce post-operative discomfort.
3. Post-Procedure Care: * Crucial for optimal healing and preventing reattachment. This typically involves specific stretches or exercises recommended by the practitioner. * For infants, immediate return to breastfeeding or bottle feeding is encouraged to help with mobility and comfort.
Do you suspect a lip tie is impacting you or your child? Don't wait to seek answers.
Consult with a qualified healthcare professional experienced in oral restrictions today. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a profound difference in comfort, development, and long-term health.
This product description provides general information about lip ties and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read here.